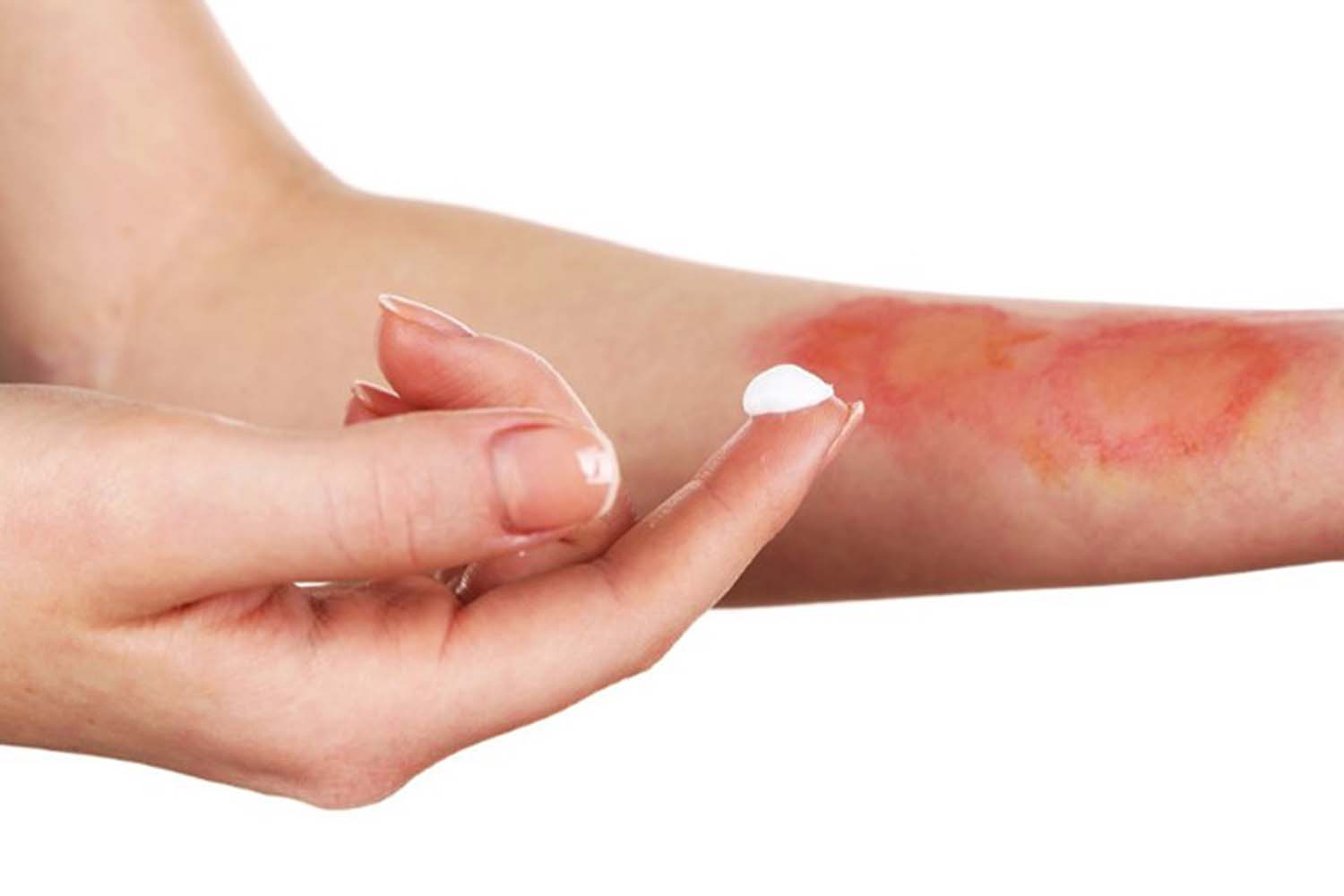
Skin burns are common injuries that can be caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, sunlight, or even cold. These injuries are divided into different degrees due to their severity and depth, and each requires its own specific care. Below, we review the types of burns, how to treat them, and tips for preventing them.
1. Types of skin burns
Burns are divided into three degrees based on severity:
- First degree burns: Only the top layer of skin (the epidermis) is damaged. This type of burn usually causes redness, inflammation, and mild pain.
- Second degree burns: The deeper layers of the skin, including the epidermis and dermis, are damaged. Symptoms include blistering and severe pain.
- Third degree burns: All layers of the skin and sometimes underlying tissues such as muscle and bone are involved. This type of burn can be painless because the nerves are damaged.
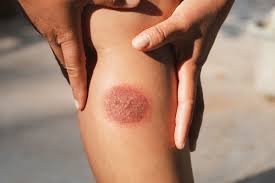
2. Common causes of burns
- Thermal burns: Caused by contact with hot objects, steam, or boiling liquids.
- Chemical burns: Contact with acids, bases or other chemicals.
- Electrical burns: Due to high voltage electric current.
- Radiation burns: Prolonged exposure to sunlight or radioactive rays.
- Cold burns: Such as frostbite caused by prolonged contact with very cold objects.

3. Methods of treating skin burns
- Treatment of first-degree burns:
- Wash the injured area with cool water to reduce the temperature.
- Use moisturizing creams or aloe vera.
- Avoid direct contact with sunlight.
- Treatment of second-degree burns:
- Using sterile dressings and changing them regularly.
- Avoid popping blisters to prevent infection.
- See a doctor in severe cases.
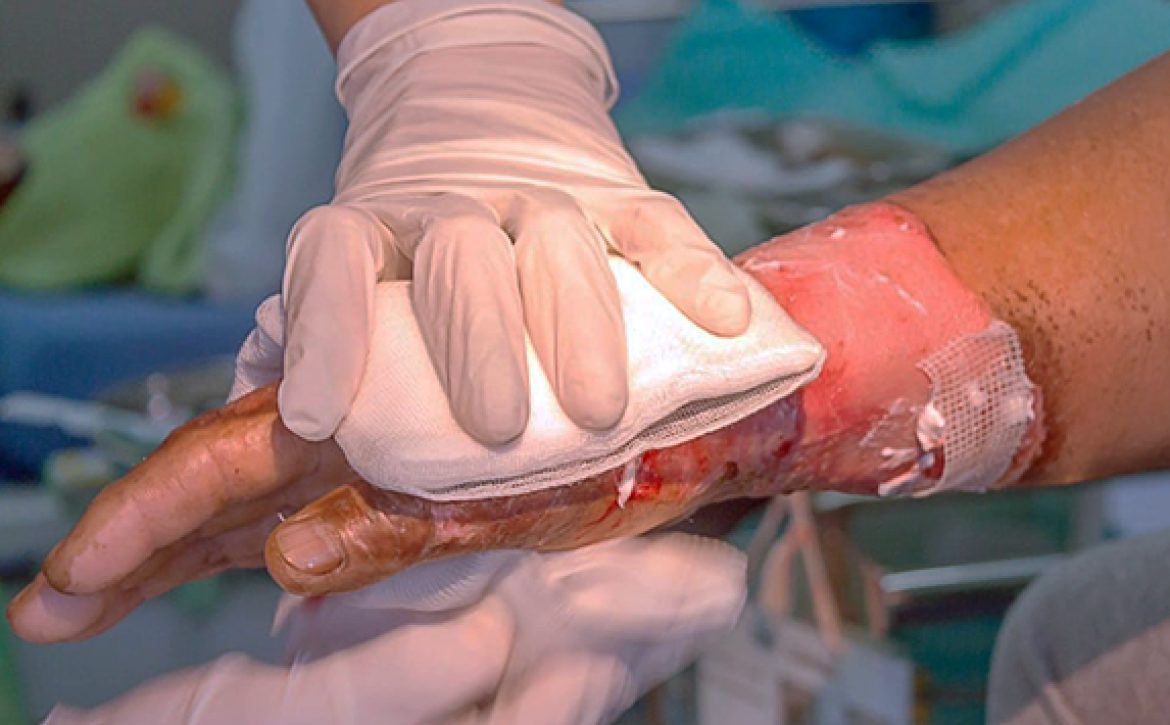
- Treatment of third-degree burns:
- Emergency care and hospital transfer.
- Using skin grafts or surgical procedures for reconstruction.
- Antibiotics and special care.
4. Preventing skin burns
- Use sunscreen with appropriate SPF.
- Observe safety principles when working with chemicals and electrical equipment.
- Wear protective clothing against radiation or hot objects.
- Keep children away from the kitchen or dangerous areas.
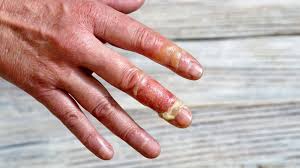
5. The latest achievements in burn treatment
Recent research shows that Biosynthetic skin And tissue regeneration methods using stem cells have shown promising results in treating severe burns. These technologies help damaged skin regenerate more quickly and reduce the chance of infection or graft rejection.
Conclusion
Although skin burns may seem minor, they can lead to serious complications if not treated properly. Understanding the types of burns, using the correct treatment methods, and following preventive tips can go a long way in reducing damage.